What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared and immutable digital ledger. It records transactions and tracks assets across a business network, creating a single source of truth. This decentralised system stores data on multiple computers, ensuring resistance to tampering and manipulation. Transactions are validated through consensus mechanisms that guarantee agreement across the network. Blockchain tech groups each transaction into a block, linking blocks into a secure and transparent chain. This structure ensures data integrity, making the technology suitable for financial, logistical and healthcare applications. Blockchain eliminates intermediaries, fostering trust and improving accountability between parties in a network.
Blockchain Explained
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain records transactions by grouping data into blocks. Each block stores details such as asset type, value and timestamp. These details include the transaction’s origin, destination, timing and specific conditions like temperature control for goods. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous block, forming an unbroken chain. This chain structure prevents retrospective modifications, ensuring data permanence. Nodes within the network validate transactions using consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. These algorithms confirm the authenticity of transactions and protect the chain from tampering. Each new block reinforces the trustworthiness of the ledger, ensuring accuracy across the system.
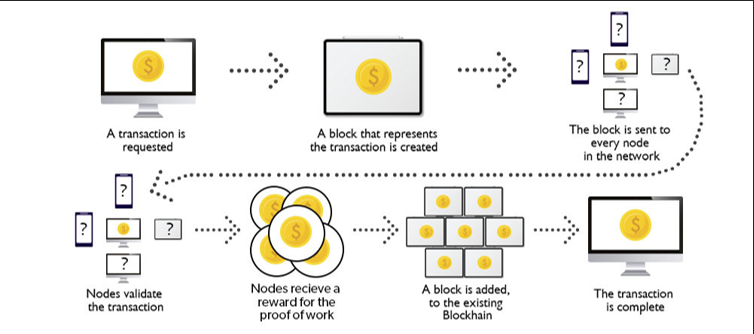
How blockchain works
The Evolution Of Blockchain
Blockchain emerged in 2008 with the creation of Bitcoin by Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced a decentralised digital currency that operates without banks. It solved the double-spending problem by using a public ledger to record every transaction. In 2015, Ethereum expanded blockchain capabilities by enabling smart contracts. These contracts automate tasks and trigger actions when conditions are met. This innovation extended blockchain’s reach into healthcare, voting, real estate and finance. Blockchain now plays a crucial role in decentralised finance (DeFi) and digital assets like NFTs. It continues evolving through integration with artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. Statista reports blockchain will grow by nearly USD 1 trillion by 2032, with a CAGR of 56.1 percent since 2021.
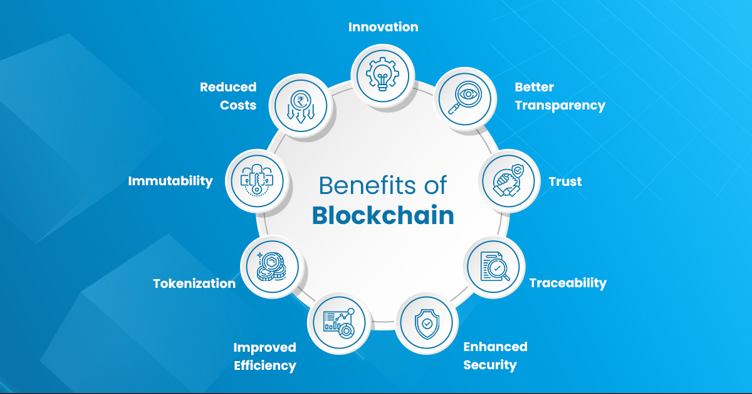
Benefits Of Blockchain
Blockchain improves trust, security and operational efficiency. It enables automated transactions and enhances traceability throughout networks.
Greater Trust:
Blockchain creates member-only networks with shared, accurate and timely data. It limits access to authorised users, increasing visibility and reliability.
Enhanced Security:
Transactions require network-wide validation. Once validated, data becomes immutable, and no administrator can delete any record.
Better Traceability:
Blockchain provides a transparent audit trail. This traceability supports sustainability goals and identifies supply chain inefficiencies.
Increased Efficiency:
With a shared ledger, blockchain removes reconciliation processes. Smart contracts automate tasks, streamlining transactions.
Automated Transactions:
Smart contracts trigger predefined actions. They reduce manual intervention and increase speed by enforcing agreed terms programmatically
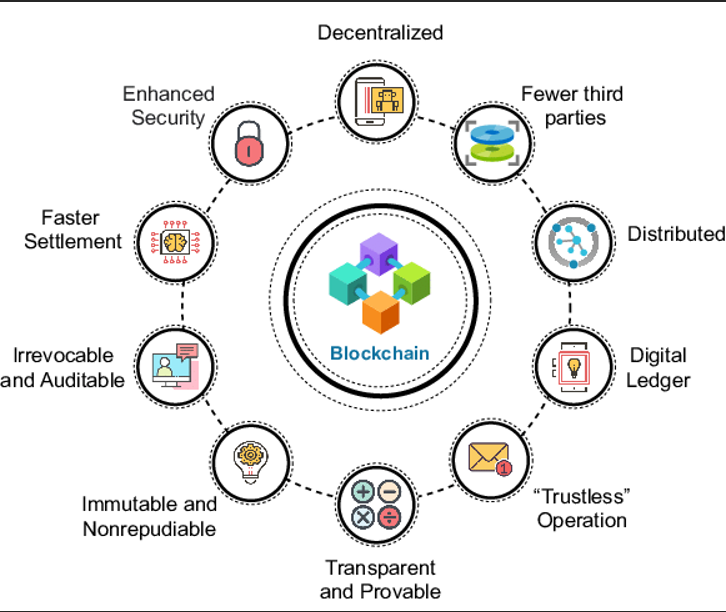
Key Features Of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain includes core features that strengthen its security and utility in data management.
Distributed Ledger Technology:
All participants access the same data, which is updated only once per transaction, preventing duplication.
Immutable Records:
After recording, transactions cannot be changed. Corrections require new entries that preserve the original record’s visibility.
Smart Contracts:
These self-executing contracts use code to enforce terms. They activate automatically when conditions are met. This feature eliminates delays and reduces third-party dependencies.
Public Key Cryptography:
Two cryptographic keys—public and private—secure blockchain transactions. The public key receives data, and the private key authorises it, ensuring both security and ownership verification.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
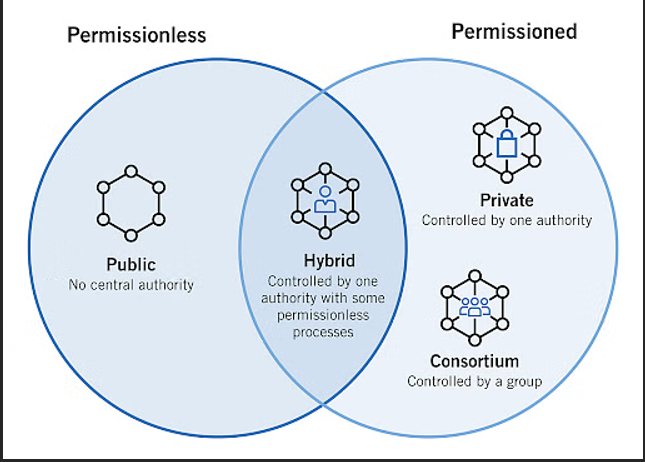
Types Of Blockchain Networks
Blockchain networks vary based on access and governance models.
Public Blockchain Networks:
Anyone can join these networks. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples. They prioritise decentralisation but may sacrifice privacy and scalability.
Private Blockchain Networks:
One organisation controls these networks. They decide who can join, validate transactions and maintain the ledger. Private blockchains offer more control and trust in closed systems.
Permissioned Blockchain Networks:
These networks restrict user participation. Both private and public blockchains can be permissioned, providing role-based access and additional security.
Consortium Blockchain Networks:
Multiple organisations collectively manage these networks. They share responsibility for validation and access. Consortium models suit sectors like energy, where shared oversight is critical.
Types of Blockchain Network
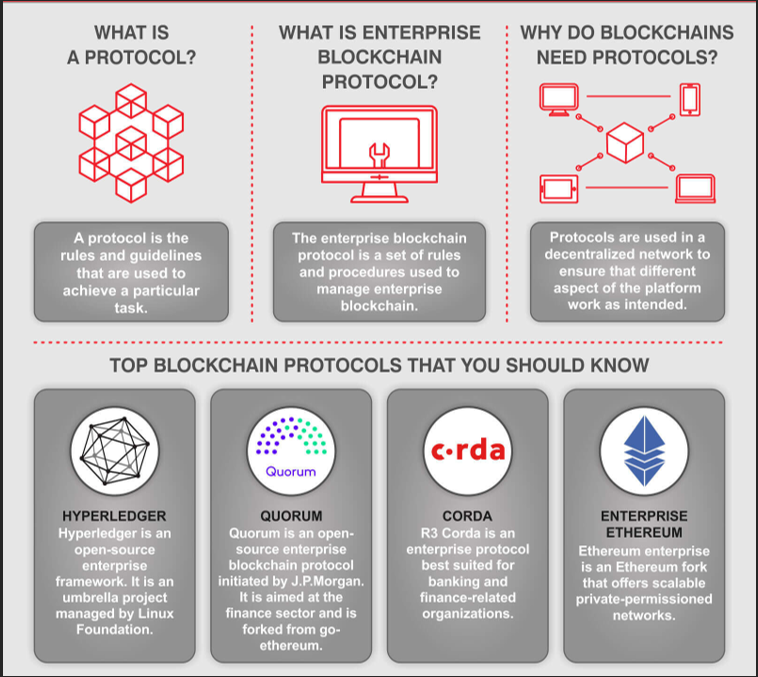
Blockchain Protocols And Platforms
Protocols define blockchain rules. Platforms enable development and deployment of applications using those protocols.
Hyperledger Fabric:
Backed by the Linux Foundation, it provides a modular architecture for enterprise-grade solutions. IBM Blockchain uses this framework.
Ethereum:
Ethereum supports smart contracts and dApps. Ethereum Enterprise targets business-specific applications.
Corda:
Corda supports private and secure business transactions. It focuses on regulatory compliance and scalability in industries like finance and healthcare.
Quorum:
Built on Ethereum, Quorum enables high privacy and speed. It supports enterprise needs, especially in financial services, with efficient consensus mechanisms.
Blockchain protocols and platforms
Blockchain And Security
Security is critical for enterprise blockchain applications. Robust security strategies involve identity access management and strong encryption. Only authorised users gain access to the system, protecting sensitive operations. Effective consensus mechanisms safeguard the network against manipulation and fraud.
Smart contracts require regular audits to detect vulnerabilities. Flawed contracts can compromise entire systems. Privacy-enhancing technologies like zero-knowledge proofs ensure compliance with regulations, including GDPR. Secure messaging protocols protect communication within the blockchain, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. Continuous monitoring and an incident response plan further reduce risk and minimise damage in case of breaches.
Blockchain in 2025
Blockchain continues to reshape industries in 2025. It offers transparency, efficiency and trust without central oversight. As blockchain tech advances, its role in securing digital economies becomes more significant. Organisations integrating blockchain must prioritise its benefits while adopting comprehensive strategies to address associated risks.












