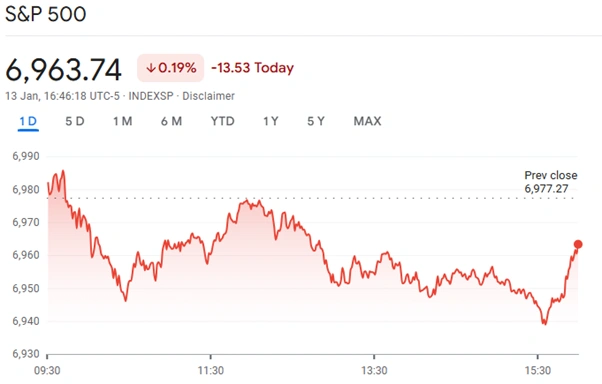
Artificial intelligence drove the S&P 500 to record levels throughout 2025. Investors now monitor signs of a significant slowdown for 2026. Capital Economics predicts the AI-fueled stock market bubble will burst this year. Equity valuations face pressure from rising interest rates and elevated inflation.
Financial analysts expect a precipitous unwinding of recent market gains. The S&P 500 reached 6,500 points during the peak of the excitement. However, current economic data suggests a correction in global equity valuations. The long-running outperformance of the United States market may soon end.
Monetary Pressures Impact Tech Growth
Higher interest rates increase the cost of capital for technology firms. Inflation remains above target levels in several major economies. These factors weigh heavily on high-growth companies. Central banks must maintain restrictive policies to combat persistent price increases.
Capital Economics expects government bond yields to settle at higher levels. This shift makes fixed-income assets more attractive than equities. US stocks might deliver average annual returns of only 4.3% through 2033. This figure sits well below the long-term average of 7% after inflation.
High Infrastructure Costs Drain Corporate Profits
Hardware and software investments reached 4.4% of US Gross Domestic Product in 2025. This level matches the height of the dot-com bubble. AI assets typically depreciate at a rate of 20% every year. Hyperscalers face annual depreciation expenses exceeding $400 billion.
These costs now surpass the combined profits of the largest technology firms. Investors worry about the sustainability of such massive capital expenditure. High electricity demands and infrastructure needs limit economies of scale. Providing a generative AI response costs ten times more than a traditional search.
Valuation Stretches Beyond Fundamental Data
The S&P 500 traded at 22.6 times forward earnings at the start of 2026. This ratio exceeds the historical median of 18 times. Market performance shows extreme concentration in a handful of technology companies. The largest firms now account for 35% of the S&P 500 index.
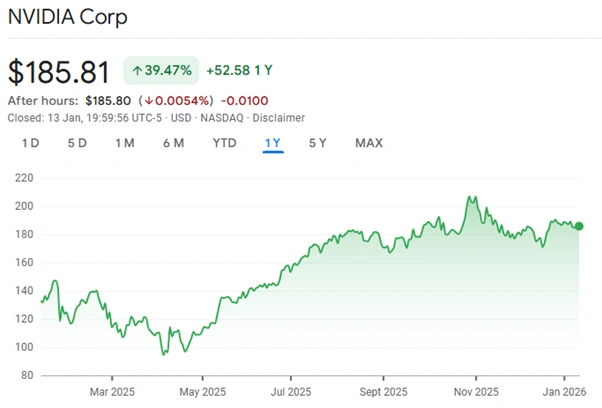
Any earnings slowdown among these leaders impacts the entire market. NVIDIA reached a market capitalisation of $5 trillion in recent trading. Its forecast revenue for 2026 represents only a small fraction of this value. Analysts label these valuations as “stretched” and “vulnerable” to sell-offs.
Supply Chain Chokepoints Restrict Hardware Sales
Deloitte predicts significant supply chain bottlenecks for semiconductor technologies in 2026. Critical tools like extreme ultraviolet lithography equipment face new trade barriers. Global spending on these technologies will exceed $30 billion this year. Export controls redefine the future of advanced logic design.
Foundries in several regions lack access to essential design software. This shortage stretches product cycles and dents corporate competitiveness. Trade restrictions affect materials, software, and assembly tools globally. Supply chain fragility remains a primary risk for hardware manufacturers.
Key Supply Chain Chokepoints:
- Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography equipment
- Electronic design automation (EDA) software
- High-bandwidth memory co-packaging tools
- Gate-all-around (GAA) transistor architectures
Adoption Rates Enter Realism Phase
Many companies remain stuck in “pilot mode” with AI projects. Allianz reports that AI rose to the second-highest global business risk. Executives cite system-reliability issues and data-quality constraints as major hurdles. Only a small share of firms extract real value from their investments.
Adoption rates for large language models show signs of moderation. Organizations face shortages of skilled talent to manage complex systems. Integration hurdles prevent the scaling of generative AI across core operations. The initial hype gives way to a more realistic implementation phase.
Also Read: Marvel Studios Releases Strategic Details Through Avengers Doomsday Teaser Campaign
Regulatory and Security Risks Intensify
New liability exposures emerge around automated decision-making and biased models. The World Economic Forum flags AI acceleration as a primary cybersecurity risk. Attackers now target AI agents and machine identities with unchecked authority. High-profile data breaches erode digital trust among consumers and investors.
Emerging AI Risks:
- Exposure of proprietary data through generative models
- System-wide errors in automated workflows
- Legal sanctions under evolving governance frameworks
- Deepfake-driven erosion of brand integrity
Regulators in several jurisdictions introduce strict guardrails for algorithmic management. These laws address concerns regarding invasive surveillance and automated firing. Compliance requirements increase the operational costs for technology providers. Legal uncertainty weighs on investor sentiment throughout the sector.
Economic Consequences of a Market Correction
A 10% drop in stock markets can reduce consumption by 0.8% of GDP. US households currently hold $65 trillion in equity wealth. A market downturn erases the wealth effect that supports consumer spending. This reversal impacts the broader economy beyond the technology sector.
BCA Research suggests the AI boom may turn to bust during 2026. The Nasdaq Composite could lose over 30% of its value in a worst-case scenario. Unemployment rates may rise as companies trim budgets and capital expenditure. Economic activity slows as the investment-led growth phase hits obstacles.
Disclaimer