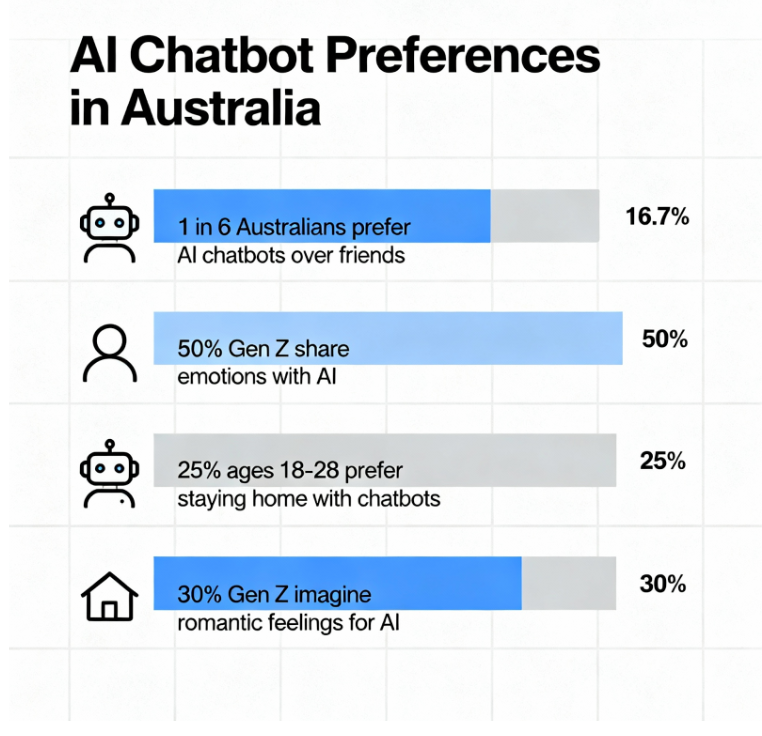
The rise of artificial intelligence chatbots appears to be accelerating the loneliness epidemic in Australia, according to new research by YouGov. The study surveyed over a thousand Australian adults and revealed that one in six respondents sometimes prefers staying at home to interact with an AI chatbot rather than going out with friends. This trend reflects a significant shift in social behaviour among Australians influenced by the availability of AI companionship.
Increasing Loneliness Linked to AI Interaction
YouGov associate director Brooke Schlesinger highlighted a surprising trend in the data. She noted that AI chatbot usage is not merely happening alongside feelings of loneliness but may be contributing to the intensification of social isolation. Younger Australians show greater openness to AI companionship, with over half of Gen Z respondents admitting they share emotional experiences with chatbots. Around 25% of those aged 18 to 28 said they sometimes prefer staying home to chat with AI instead of socialising in person.
The study further revealed close to 30% of Gen Z participants could imagine developing romantic feelings for an AI chatbot. The scale of this sentiment is broad, encompassing millions of Australians, indicating that romantic relationships with AI are increasingly considered plausible beyond fiction. This points to profound changes in how social and emotional needs are met in the digital era.
Statistics on AI chatbot usage and loneliness trends among Australians
Psychological Risks and Social Implications
Experts caution that while AI chatbots provide comfort and support, there are psychological risks involved. Professor Mansell emphasised that loneliness often stems from root causes such as fears, anxieties, and unresolved relationship issues. He noted that AI companionship can offer solace but may also delay individuals from addressing these deeper concerns through human interaction. There is a risk that over-reliance on AI leads to withdrawal from socialisation and delays in seeking professional help.
Julie Inman Grant, eSafety Commissioner, warned about the design of AI companions that intentionally foster emotional attachment. By mimicking human qualities and offering constant affirmation, these chatbots can create a false sense of deep connection which may reinforce loneliness instead of alleviating it.
Benefits and Limitations of AI Chatbots in Mental Health
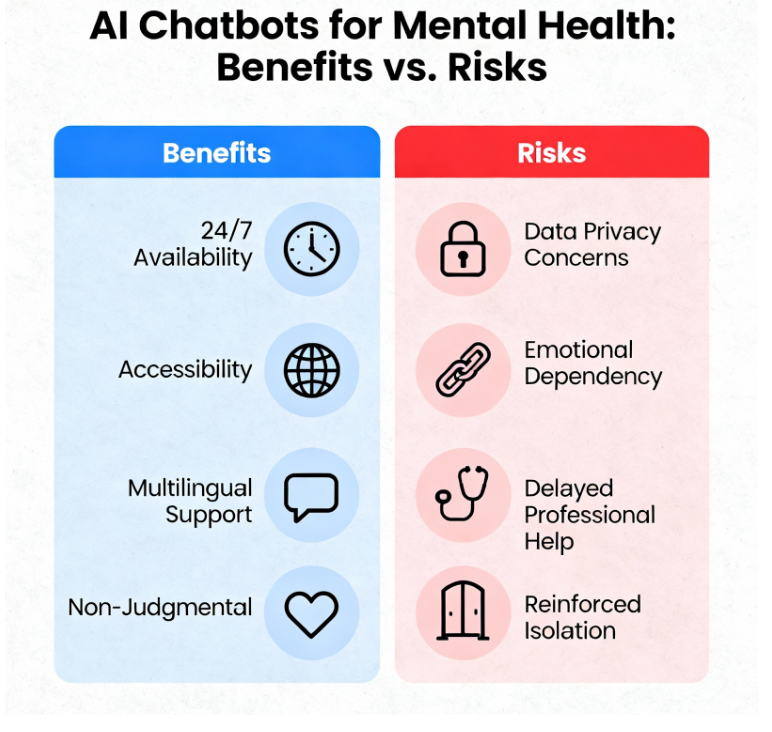
Mental health clinicians acknowledge the dual nature of AI chatbots. While chatbots can increase accessibility to support and offer 24/7 availability, clinicians worry about their limitations. A study from the University of Melbourne involving mental health professionals identified benefits such as helping with homework assignments, multilingual support, and non-judgmental interactions that improve client engagement. However, clinicians also pointed out risks including data privacy concerns, limited understanding of individual client backgrounds, and the potential for clients to rely excessively on AI.
The clinicians emphasized that AI chatbots are suitable only for non-critical tasks and stressed the necessity of human oversight. They identified the inability of AI to interpret subtle social cues as a significant drawback. There is also concern that AI may inadvertently reinforce maladaptive beliefs by prioritising user satisfaction over therapeutic truthfulness.
Benefits and risks of AI chatbots in mental health support
Widespread Use Among Young Australians
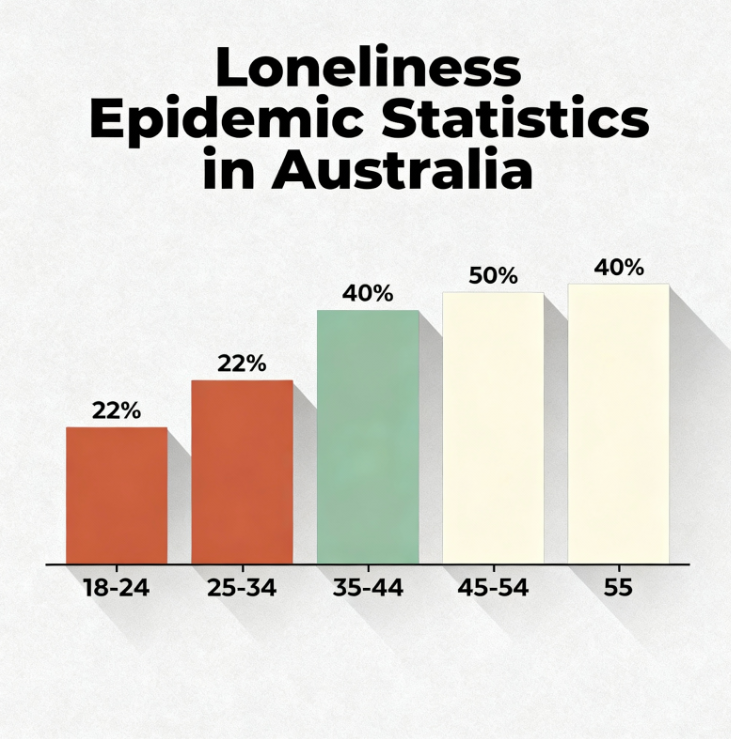
The rise in AI companion usage is most marked among younger Australians. According to the YouGov survey, the loneliest demographic aged 18 to 24 has seen loneliness rates spike from 22% to 40% in recent years. Many in this group use AI chatbots for emotional support and as a means to navigate social and personal challenges. For example, a musician in Victoria reported using a chatbot as a “sounding board” to work through problems before reaching out to friends. This indicates a blending of AI companionship with traditional social supports.
Rising loneliness rates among young Australians aged 18 to 24
Government Attention and Regulatory Concerns
The Australian government and regulatory bodies like eSafety are paying close attention to the risks associated with AI chatbots. There are calls for clearer guidelines and education to ensure people understand potential harms. The rapid deployment of AI without comprehensive clinical efficacy trials heightens concerns about privacy, misinformation, and emotional well-being.
Experts advocate for embedding AI services within existing mental health frameworks to provide safeguards and improve outcomes. Policymakers face the challenge of balancing innovation with protecting vulnerable populations from over-dependence on technology.
Final Remarks
The new YouGov study underscores a transforming social landscape in Australia, where AI chatbots increasingly fulfil emotional and social roles for many individuals. While these technologies offer advantages such as accessibility and non-judgmental support, their role in accelerating loneliness demands careful scrutiny. Mental health professionals call for regulated, cautious integration of AI chatbots with human oversight, to ensure these tools supplement but do not replace essential human connections. As loneliness rates rise, particularly among young Australians, the balance of technological support and real-world interaction becomes critical to public health.