Government Support Fuels New Exploration Activity
New South Wales Government is progressing on its goal to be a major player in global critical minerals supply chains. A recent funding program has provided 29 exploration projects in the state by allocating the funds of 5 million dollars. The grants are to help companies that carry out the drilling, geophysics, and geochemistry activities, but with the aim of discovering new deposits of resource of high resources.

This investment is in line with the rising world demand for materials to be used in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, smartphones, and other contemporary technologies.
The funds have been used to speed up the exploration programs of several companies that include Waratah Minerals, Neo Double Eagle Resources, Alkane Resources, and Silverton Minerals. Such activities are the first stage of a long development process to establish the viability of new mining activities.
Having a strategic presence of minerals has increased the relevance of the world
New South Wales has a rich collection of minerals that are deemed to be crucial to world industries. NSW leads the emerging clean energy ecosystem since 21 of the 31 minerals on the national list of critical minerals in Australia are found there. The rare earth elements, copper, and specialised metals deposited by the geological structure of the region are required in the production of specialised electronics, wind turbines, electric motors, and batteries.
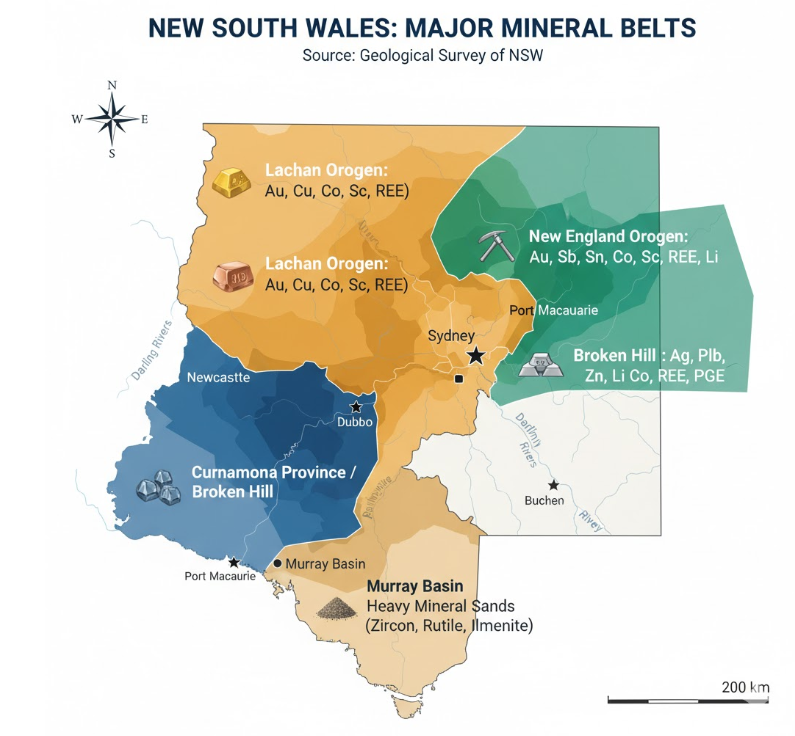
NSW hosts 21 of the 31 nationally recognised critical minerals, giving the state an unmatched geological advantage
Such wide diversification of types of resources enables the state not to be overly dependent on a single commodity. With the increase in international competition, it is likely that those jurisdictions that are multi-sector appropriate will be more resilient.
Economic Strategy Objective is to bring in Investment
According to government modeling, the development of the critical minerals will spur regional development, create employment, and enhance faster infrastructure development. Through prioritisation of projects within the regional communities, it is projected that the investment will also help in transport, logistics, and service industries that are associated with mining activities. The aggregate influence in these sectors will generate a multiplier effect that will lead to economic stability.
The financial mechanisms have been established to encourage the participation of the private sector by giving support to the companies at their early stages of development. These incentives reward the high capital needed in exploration, environmental evaluation and specialised processing facilities.
International Supply Demand Gives Copper and Rare Earth a boost
The growth in copper production in NSW has been more than one-third in the last three years, which reflects both the favorable market conditions and the improvement in operations at the existing sites. This burst is associated with pressure on the world stock because the production of electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure is growing.

Moreover, rare earth components are also vulnerable to the international supply chain risk because it has few producers. They are used in permanent magnets, electronic components, and aerospace technology, which raises strategic interest.
With increasing demand, the NSW producers will be in a position to market to the international market due to the need to find reliable and stable political sources of material.
Government undertakes to cut Regulatory Barriers
The state has demonstrated its intentions by highlighting the state at the International Mining and Resources Conference, where Premier Chris Minns said that NSW is open for business concerning critical minerals. He accepted the fact that the current planning processes have led to duplication, as well as regulatory delays.
This system is under consideration to be improved and made more efficient, and to give the investors better timelines. The government would ensure that the environment remains at the desired level, but provides a smoother approval route.
Materials Are Strategic in Support of National Security Objectives
Other than commercial use, some of the minerals found in NSW are listed as strategic because of their use in defence and aerospace technologies. Four out of five minerals in the strategic minerals list in Australia are found in the state, which makes NSW crucial in national supply chains planning. Such resources are applied in defence electronics, precision components, and high-tech propulsion systems.
Also Read: Lovisa Global Store Expansion 2025 Strengthens International Retail Footprint
Final Thoughts
New South Wales is also taking advantage of its superior geological resources, favorable investment framework, and government coordination to emerge as a global critical minerals powerhouse. The state of strategy positions it in a favourable position with increased global demand for the production of electrification and renewable energy sources. The success of NSW in utilising this opportunity will depend on further investigations, the regulation of the situation, and the developments on a downstream level.
FAQs
- What are critical minerals?
Critical minerals are metallic or non-metallic elements essential for modern technologies, economies, or national security, and their supply chains are considered vulnerable or limited.
- Why is New South Wales investing in critical minerals exploration?
NSW is investing to leverage its geological strengths, support the global clean energy transition, attract private investment, and stimulate regional economic activity.
- What funding has the NSW Government provided for exploration projects?
The government has committed $5 million to support 29 exploration projects involving drilling, geophysics, and geochemistry to identify new resource deposits.
- Who is eligible to apply for critical minerals exploration funding in NSW?
Eligible applicants generally include registered companies, incorporated associations, and approved entities that hold relevant exploration titles and meet financial and compliance requirements.
- What types of exploration projects can qualify for funding?
Funding supports activities such as drilling programs, geophysical surveys, and geochemical sampling that contribute meaningful insights into potential mineral deposits.
- Which minerals are targeted by the program?
The program focuses on minerals classified as critical and strategic, including rare earth elements, copper, scandium, silver, and other high-tech metals.
- Are there deadlines for completing funded exploration work?
Most funded exploration projects must be completed within defined timelines set by program guidelines to ensure accountability and measurable outcomes.
- How will critical minerals investment benefit regional NSW communities?
The investment is expected to create jobs, support local businesses, improve infrastructure, and generate long-term economic growth in mining-focused regions.
- How does NSW compare globally in the critical minerals sector?
NSW holds a strong position due to its diverse mineral inventory, stable regulatory framework, skilled workforce, and established mining industry experience.
- Why are rare earth elements important to modern industries?
Rare earth elements are used in electric vehicle motors, wind turbine magnets, aerospace systems, and advanced electronics, making them essential to clean energy and defence sectors.
- Why is copper demand increasing?
Copper is heavily used in electric vehicle components, renewable energy systems, power transmission networks, and modern electronics, which drives global procurement pressure.
- How is the NSW Government improving regulatory barriers?
The government has committed to streamlining planning systems and reducing duplication to create faster and more predictable project approval timelines.
- What role do critical minerals play in national security?
Critical minerals support defence technologies, aerospace manufacturing, secure communication systems, and advanced weapon guidance platforms, making supply reliability a strategic priority.
- What challenges does the critical minerals sector face?
Challenges include commodity price volatility, environmental concerns, complex permitting, high capital requirements, and long development lead times.
- How does exploration funding support early-stage mining operations?
Exploration funding helps companies offset upfront costs associated with technical surveys, scientific analysis, drilling programs, and feasibility work before moving to development stages.