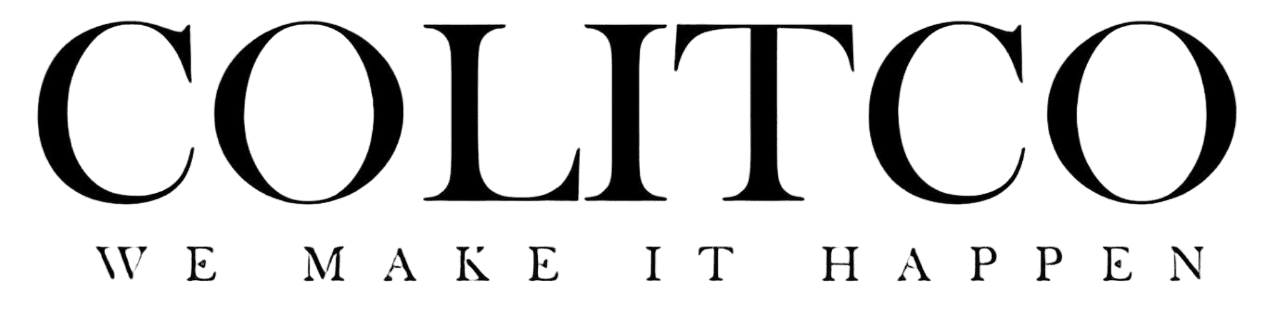Scientists from NASA and research institutions have proposed using nuclear explosions to destroy asteroid 2024 YR4. The 60-metre-wide space rock poses a significant threat to lunar missions and Earth-based operations. International researchers published findings suggesting nuclear disruption represents the most viable defence option.
The asteroid measures approximately 200 feet in diameter according to James Webb Space Telescope observations. Scientists initially calculated Earth impact probability at 3.1% for December 2032. Subsequent analysis ruled out Earth collision but confirmed a 4.3% lunar impact chance.
Asteroid 2024 YR4 threat assessment and specifications
Nuclear Mission Specifications
Proposed Nuclear Devices
Researchers recommend deploying two 100-kiloton nuclear devices capable of autonomous space navigation. Each device delivers five to eight times the explosive power of atomic bombs dropped on Nagasaki and Hiroshima in 1945. The mission includes backup explosives stored onboard spacecraft in case primary devices fail.
Nuclear disruption missions could launch between late 2029 and late 2031 according to orbital mechanics calculations. Scientists favour nuclear options over kinetic impactor missions due to mass uncertainty factors.
Mission Timeline Constraints
The team identified limited reconnaissance opportunities before asteroid interception deadlines. Late 2028 represents the optimal launch window for preliminary survey missions. This timeline provides only three years for mission development and spacecraft construction.
Nuclear disruption missions offer five to seven years development time compared to reconnaissance alternatives. The extended preparation period allows comprehensive testing and system verification procedures.

Nuclear asteroid deflection mission timeline and specifications
Technical Challenges and Uncertainties
Mass Calculation Problems
Asteroid 2024 YR4 mass estimates range from 72.7 million to 2 billion pounds creating significant mission planning complications. Scientists require precise mass data for accurate deflection calculations and nuclear device specifications. Incorrect mass assumptions could redirect the asteroid toward Earth rather than away from collision paths.
James Webb Space Telescope provided diameter measurements but density remains unknown. Surface composition analysis indicates probable S-type stony asteroid classification. Rotation period calculations show approximately 19.5-minute cycles.
Alternative Defence Options
Kinetic impactor missions similar to NASA’s successful DART program remain under consideration. The 2022 Double Asteroid Redirection Test demonstrated spacecraft capability to alter asteroid trajectories through high-speed collisions. DART impacted Dimorphos asteroid at 14,000 miles per hour successfully changing its orbital period.
Researchers assessed gravity tractor concepts involving spacecraft gravitational influence on asteroid paths. Ion beam propulsion systems offer continuous thrust applications over extended periods. Surface modification techniques include reflectivity alterations through spray painting methods.

Comparison of asteroid defence strategies and their capabilities
Lunar Impact Consequences
Debris Field Projections
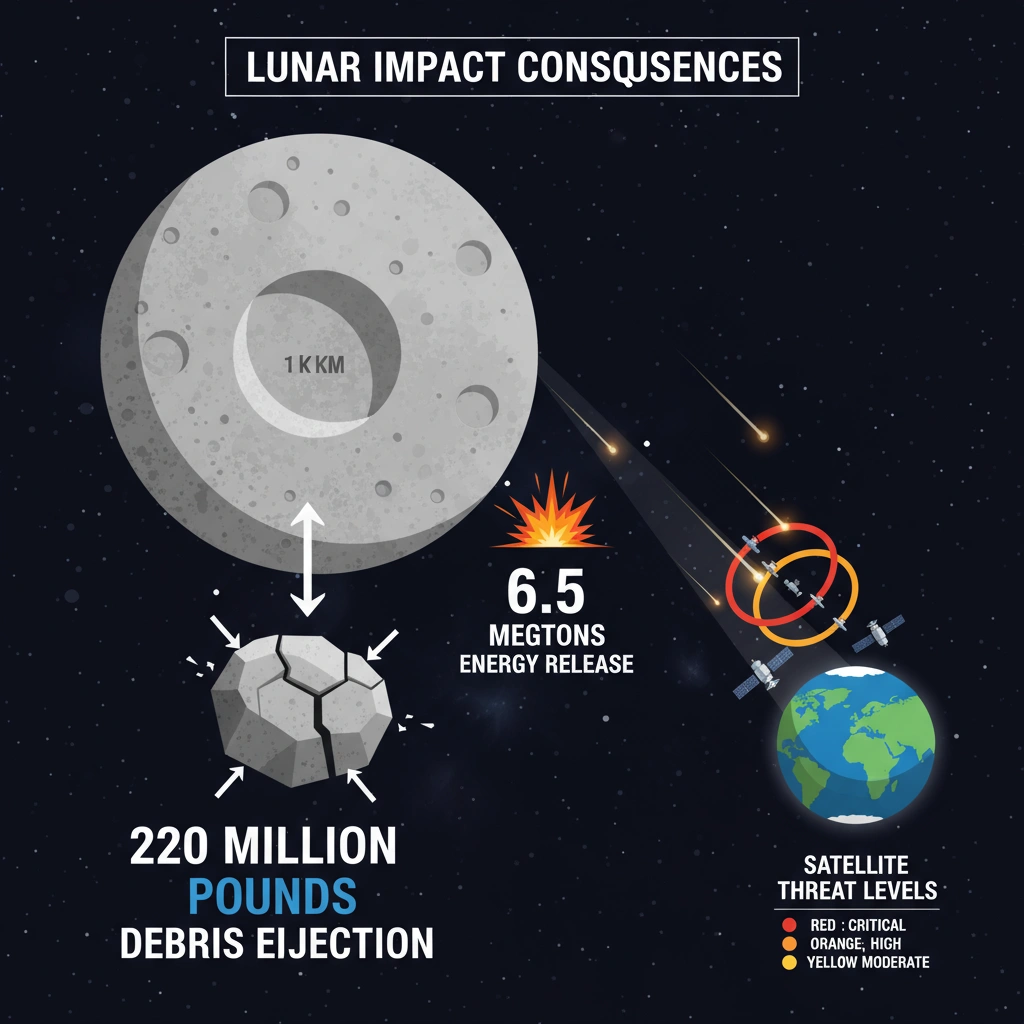
Lunar impact scenarios project up to 220 million pounds of surface material ejection into space. Computer simulations indicate 10% of debris could reach Earth’s gravity well within days of collision. Micrometeoroid flux increases could exceed background levels by 1000 times.
The impact would create a one-kilometre-diameter crater releasing 6.5 megatons of TNT equivalent energy. Satellite operations face significant disruption from increased debris particle density. International Space Station astronauts require enhanced protection protocols during debris shower periods.
Earth-Based Observations
Ground telescopes would observe spectacular meteor shower displays following lunar impact events. Debris particles entering Earth atmosphere create visible light phenomena across multiple continents. Scientific observation opportunities include composition analysis of lunar material samples.
Projected consequences of Asteroid 2024 YR4 lunar impact scenario
International Policy Implications
Treaty Considerations
Nuclear weapon deployment in space faces restrictions under Outer Space Treaty provisions. International law prohibits nuclear explosives beyond Earth atmosphere except for peaceful purposes. Planetary defence applications require careful legal framework development.
United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs coordinates international asteroid threat responses. Space agencies must achieve consensus on nuclear deployment protocols before mission authorisation. Diplomatic negotiations determine command structure and oversight mechanisms.
Budget and Resource Allocation
NASA operates under significant budget constraints affecting mission feasibility assessments. Congressional funding approval requires demonstration of clear threat levels and mission success probability. Cost-benefit analysis compares nuclear disruption expenses against potential damage prevention.
Current asteroid poses minimal Earth impact risk potentially limiting political support for expensive nuclear missions. Resource allocation priorities favour confirmed threats over speculative scenarios.
Future Monitoring Requirements
Scientists plan continued asteroid tracking through 2028 when observation conditions improve. Additional telescope observations will refine impact probability calculations and trajectory predictions. Mission planning proceeds simultaneously with monitoring activities to ensure rapid response capability.
The international scientific community maintains asteroid 2024 YR4 represents valuable testing opportunity for planetary defence systems. Nuclear disruption techniques require validation before larger threats emerge.