Blockchain’s Foundation Emerged in the Early 1990s
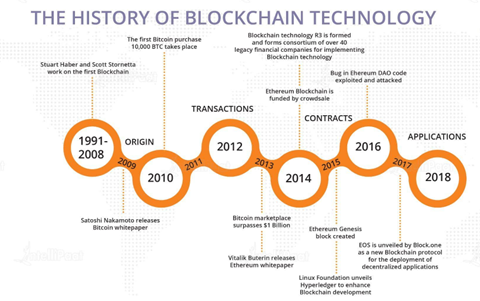
The history of blockchain technology dates back to 1991, when Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta published a piece on a cryptographically secured chain of block. It is impossible to think about a person who can change document timestamps on their system. They added Merkle trees in 1992 to be more efficient and to include more documents in a block.
This paved way to evolution of the technology. The real world applicability of blockchain began in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto embarked on Bitcoin. Nakamoto came up with a decentralised system that works in blocks to increase the digital trust without intervention of authorities.
Timeline of Blockchain’s historical events
Blockchain Structure: Core Mechanisms Behind the Technology
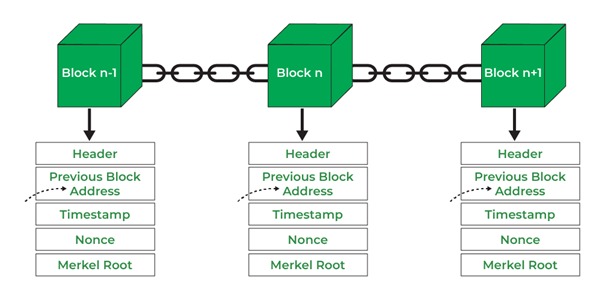
Blockchain can be characterized as a distributed ledger that is used by network members. It is structured in peer-to-peer format with autonomous control and time stamping servers. Every block contains authorized transaction batches and has a cryptographic hash value of the former block.
The participant is allowed to add new blocks though he cannot alter the existent records. Transparency of the system guarantees data of all the users to be the same. This technology allows decentralized trusting collaboration, without central control.
Blockchain’s First Application: Bitcoin
In 2009 Satoshi Nakamoto published the whitepaper of Bitcoin, describing how an independent peer-to-peer system will be possible. This was launched in that year, in what started the first blockchain in the real world with the genesis block. Connected cryptographically to the other one, each mined block created an immutable and safe chain.
Bitcoin employed blockchain technology to verify and record peer to peer transactions. This came in with blockchains and the possibilities of decentralised/trustless systems that are not confined in the financial world.

Bitcoin was Blockchain’s first application
The Evolution of Blockchain Technology
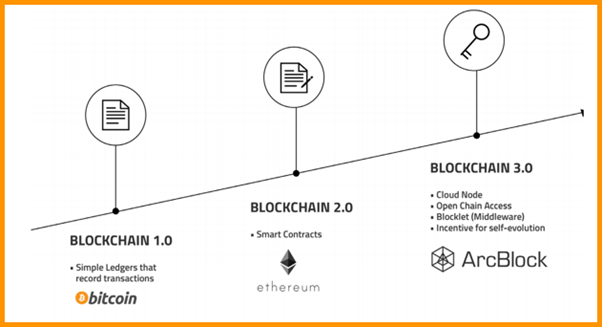
Blockchain 1.0: Peer-to-Peer Transactions and Bitcoin’s Emergence
The main use of blockchain between 2008 and 2013 was facilitating the transactions of cryptocurrency. Bitcoin was the demonstration of blockchain as a ledger that was being used in the absence of a centralized authority. All the transaction data was stored in the blockchain making an impenetrable record.
The launch of Bitcoin expressed the utility of digital ledgers. It gave rise to the development of such assets and cryptocurrencies. Blockchain became popular when developers thrived to find other applications of distributed ledger.
Blockchain 2.0: Smart Contracts Expand Capabilities
Ethereum was launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin who discovered the shortcomings of Bitcoin. He desired a blockchain platform that can do more than transfer of multiple cryptocurrencies. The Ethereum launched by Buterin was based on programmable smart contracts.
Ethereum gave rise to users being able to record other assets and execute smart contracts. Developers started creating decentralised applications within the blockchain of Ethereum. It rapidly gained the status as the most dynamic blockchain in terms of transactions.
The capacity to run smart contracts brought forth new uses of blockchain in Ethereum. These were gambling, money, and a non-centralised government.
Blockchain 3.0: New Platforms and Wider Adoption
The year 2018 marked a new period in blockchain as different platforms became popular. The developers aimed at adding scalability, efficiency, and industry application. NEO came out as the Chinese open-source blockchain system. In spite of crypto bans, China warmed to blockchain development.
Such people as Jack Ma of Alibaba supported NEO. It empowered smart contracts and digital assets in a manner equivalent to Ethereum. IOTA came out of the scene with no transaction fee in the Internet of Things ecosystem.
Monero, Zcash and Dash focused more on the privacy of transactions. Such privacy coins offered higher security record than Bitcoin and Ethereum. They have enabled the blockchain platforms to be diverse to accommodate various user requirements.
Evolution of Blockchain
Hyperledger Brings Industry Collaboration in 2015
In 2015, Linux Foundation initiated a research project on Hyperledger to encourage open-source blockchain growth. Hyperledger under the leadership of Brian Behlendorf allowed the cross-industry collaboration. The project was aimed at constructing global business transaction tools.
The development of hyperledger favored blockchain systems used in enterprises. Companies started to investigate how the use of blockchain can help streamline its operations. Those initiatives resulted in the emergence of private, hybrid and federated blockchains.
EOS.IO Launches Decentralised Operating System in 2017
In 2017, Block.one published a whitepaper of EOS.IO. The protocol presented a decentralised operating platform that runs on EOS cryptocurrency. EOS.IO copies up the actual computing assets such as GPU and CPU.
Such system made it possible to deploy applications in decentralised form at a very high speed. It enabled massive run of smart contracts. EOS.IO was designed to improve performance of enterprise blockchain utilization.
Also Read: Bitcoin Smashes $116K as Trump Renews Fed Rate Cut Calls, Ignites Crypto Surge
2020 Onwards: Future Growth and Government Interest
Since 2020, governments and business enterprises invested more in blockchain. They discussed how it was used in cloud computing, supply chains and automation. It was the view of analysts that blockchain would lead to tremendous changes in how the systems are run in the day-to-day life.
Gartner predicted that at least one blockchain-powered business will have a value over 10 billion USD in 2022. There could be a total business value of blockchain of up to $176 billion by the year 2025. Investment analysts projected this number to increase to the tune of $3.1 trillion by 2030.
The role of the blockchain technology changed globally with companies employing the experts. Companies used blockchain to trace a commodity, automate, and have data integrity. This increasing need of block chain professionals proved out the fact about evolution of the technology.
Private Blockchains Offer Enterprise Efficiency
Enterprises adopted private and hybrid blockchains to streamline operations. Unlike public blockchains, private networks restrict access to approved participants. Companies like Microsoft led the way in developing internal blockchain systems.
Private blockchains offered performance benefits for regulated industries. They provided tailored solutions without sacrificing security. This shift marked another step in blockchain’s broader enterprise adoption.
Blockchain’s Growing Role in Digital Economies
The evolution of blockchain reflects increasing adoption across sectors. From timestamps to decentralised applications, the technology has transformed rapidly. Bitcoin introduced the digital ledger concept, while Ethereum expanded functionality with smart contracts.
Platforms like NEO, IOTA, and EOS.IO continued the innovation wave. Government and enterprise investment signalled blockchain’s central role in future economies. Blockchain’s evolution created demand for professionals and spurred new industry applications.