Australia’s mining sector accelerates towards net-zero emissions through groundbreaking technologies and strategic investments. The industry targets the complete elimination of fossil fuel dependency by 2050.
Mining Giants Commit $50 Billion to Clean Energy Transition
Major Australian mining companies have committed unprecedented funding to decarbonisation initiatives. BHP allocated $2 billion for electrification systems between 2022 and 2025. Rio Tinto pledged $7.5 billion towards renewable energy infrastructure through 2030. Fortescue Metals Group leads the sector with $6.2 billion dedicated to eliminating fossil fuels by 2030.
The mining sector contributed 99 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2022. This represented 23 per cent of Australia’s total national emissions. Industry leaders recognise the urgency of transformation to meet climate targets.
Australia maintains a national target of 43 per cent emissions reduction by 2030 compared to 2005 levels. The country aims for net-zero emissions by 2050. Mining companies must deliver substantial reductions to support these objectives.
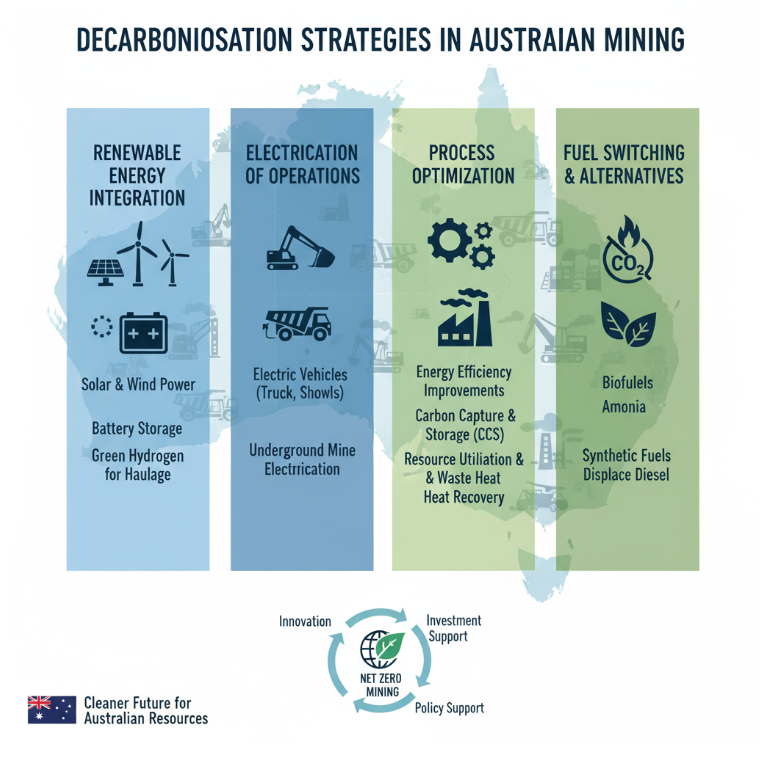
Decarbonisation Strategies Overview
Renewable Energy Powers Mining Operations Nationwide
Solar and wind energy installations transform mining sites across Australia. Gold Fields announced a $195 million renewable energy project for its St Ives Gold mine in Western Australia. The facility will supply renewable electricity to reduce operational emissions.
Rio Tinto developed a 34MW solar farm at the Gudai-Darri iron ore mine. The installation provides up to 65 per cent of electricity needs during peak solar production periods. Such projects demonstrate the viability of renewable integration at remote mining locations.
Renewable energy adoption can reduce operational carbon emissions by up to 50 per cent within one year. Mining companies leverage Australia’s abundant solar resources to achieve these reductions. The Agnew Gold Mine achieved 80 per cent renewable penetration through wind turbines, solar arrays, and battery storage.
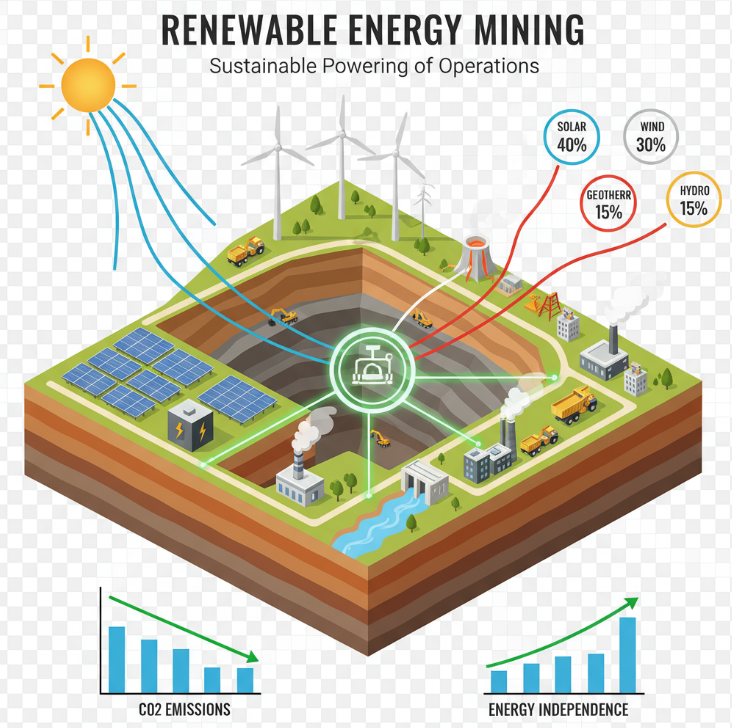
Renewable Energy Integration
Electric Vehicle Fleets Replace Diesel Equipment
Mining companies rapidly electrify their vehicle fleets to eliminate diesel emissions. BHP deployed over 200 electric light vehicles across Western Australian iron ore operations. The company plans expansion to include electric heavy equipment across multiple sites.
Electric mining equipment reduces operational costs by 10 to 20 per cent compared to diesel alternatives. The Mt Marion Lithium Project invested $46 million in electrification and achieved 23 per cent operational expense reduction. Maintenance costs decrease by 25 to 30 per cent due to simpler electric systems.
Underground mines particularly benefit from electrification initiatives. Electric load-haul-dump machines eliminate diesel particulate matter in confined spaces. Air contamination drops from 50 micrograms per cubic metre to less than one microgram.
Fortescue signed a $2.8 billion agreement with Liebherr to create zero-emission mining fleets. The partnership focuses on battery-electric mining equipment for heavy-duty applications. Such collaborations advance technology development for Australian conditions.

EV Fleet Adoption
Battery Technology Advances Enable Heavy Equipment Transition
Modern lithium-ion batteries withstand extreme mining environments including temperatures exceeding 50 degrees Celsius. Thermal management systems extend battery life by up to 40 per cent in harsh conditions. These improvements support reliable operation in remote Australian mining regions.
Fast-charging systems delivering 350 kilowatts deploy at strategic mine locations. High-power charging stations add 25 per cent to upfront costs but reduce lifetime expenses by 40 per cent. Improved equipment utilisation offsets initial investment requirements.
Battery swap systems offer alternatives for continuous operations requiring 24-hour availability. Automated exchange stations replace depleted batteries in under 10 minutes. This approach maintains productivity while supporting full electrification.
ARENA provided $9 million to BluVein for dynamic charging technology trials. The “hammer and rail” system enables safe electric powering while vehicles remain in motion. This innovation addresses power requirements for ultra-class heavy haulage trucking.
Green Hydrogen Development Targets Heavy Transport
Fortescue pursues green hydrogen production to power equipment unsuitable for battery electrification. The company focuses on replacing diesel in heavy mobile equipment through hydrogen fuel cells. Green hydrogen offers zero-emission alternatives for the most demanding applications.
Hydrogen technology addresses energy density limitations of current battery systems. This makes hydrogen ideal for large-scale heavy-duty mining trucks requiring extended operation periods. Early investments ensure energy supply security and regulatory compliance.
The technology involves converting water into hydrogen using renewable energy sources. Hydrogen-powered fuel cells provide emission-free alternatives for stationary equipment and material transport. Hybrid hydrogen-diesel systems bridge current gaps while infrastructure expands.

Usage of Green Hydrogen
Carbon Capture and Storage Projects Launch Across Australia
Australia develops 16 geological storage projects across multiple states. The Gorgon CCS project on Barrow Island represents Australia’s first commercial-scale operation. The facility stored over 9 million tonnes of carbon dioxide between 2019 and 2023.
Santos completed construction of the Moomba CCS facility in the Cooper Basin. The project began injection operations in 2024 with capacity for 1.7 million tonnes annually. This represents more than 7 per cent reduction in South Australia’s total emissions.
Australia possesses enormous theoretical capacity for geological carbon storage. Oil and Gas Climate Initiative estimates 31 gigatonnes of sub-commercial storage capacity. Undiscovered storage resources total approximately 470 gigatonnes across sedimentary basins.
Carbon capture enables mining companies to reduce emissions from industrial processes. The technology captures carbon dioxide from power generation and transports it to underground storage sites. Permanent storage provides viable solutions for hard-to-abate emissions.
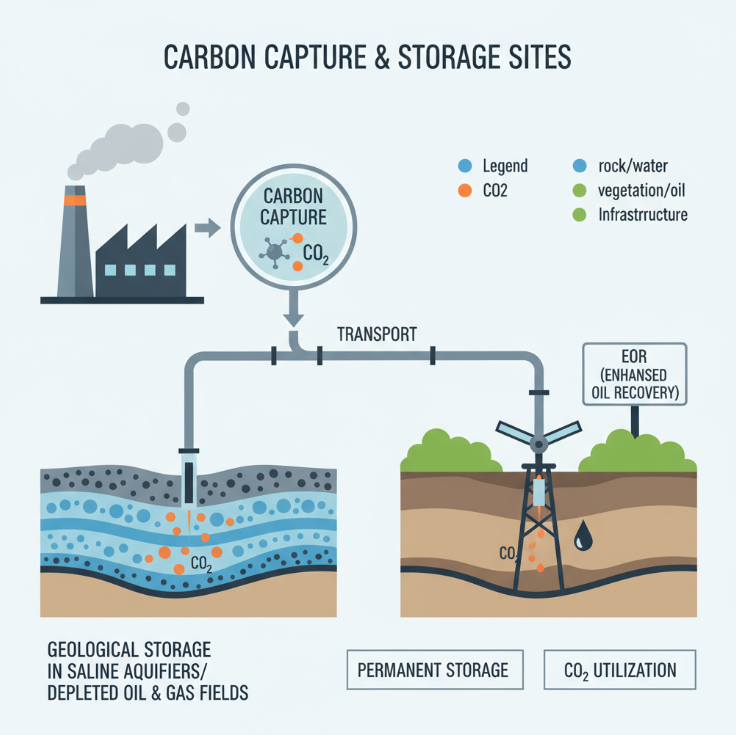
CCS Projects
Autonomous Systems Integrate with Electric Fleets
Rio Tinto implements autonomous electric haulage systems at multiple mining sites. Early trials indicate productivity improvements of 15 to 20 per cent over conventional diesel equipment. Autonomous systems combine electrification benefits with reduced labour costs.
AutoHaul autonomous trains demonstrate potential for combining automation with digital integration. These systems travelled over 7 million kilometres autonomously since implementation. Mining companies extend autonomous capabilities to battery-electric vehicle fleets.
Electric conveyor systems replace diesel truck haulage for material movement. The Pilgangoora Lithium Project utilises extensive electric conveyor networks eliminating 26 diesel haul trucks. Energy savings reach up to 85 per cent for comparable transport distances.
Renewable Energy Statistics Show Rapid Growth
Australia generated 25 per cent of electricity from solar power in October 2024. This marked the first time solar provided a quarter of national electricity generation. Combined wind and solar reached 40 per cent of electricity supply.
Rooftop solar installations achieved 24.4 gigawatts of cumulative capacity in the first half of 2024. Australia tracks towards exceeding 25 gigawatts by year end. Rooftop photovoltaic capacity already surpassed coal generation capacity of 21.3 gigawatts.
Renewable energy extraction increased 12 per cent to 325 petajoules in 2022-23. Solar and wind generation quadrupled since 2015 across Australia. This growth provides clean electricity for mining operations transitioning from fossil fuels.
Infrastructure Investment Supports Decarbonisation Goals
Mining companies invest heavily in power infrastructure upgrades supporting electrification. Rio Tinto allocated $7.5 billion for grid improvements across Australian operations. Remote mine sites require significant infrastructure development for renewable integration.
Microgrids combining renewables with battery storage become standard for new projects. These systems balance load demands across multiple power sources optimising cost and reliability. Virtual microgrids demonstrate intelligent load management capabilities.
Grid connection challenges necessitate innovative power solutions in remote locations. Mining companies pioneer localised renewable generation and storage systems. Some Western Australian operations implement virtual microgrids for enhanced efficiency.
Industry Emissions Reduction Targets Drive Innovation
Australian mining companies typically target 30 per cent emissions reduction by 2030. Most miners established 2050 as the deadline for achieving net-zero carbon emissions. Fortescue leads with aggressive 2030 carbon neutrality commitment.
BHP achieved its 2030 target of 30 per cent operational emissions reduction ahead of schedule. The company reduced Scope 2 emissions through renewable energy power purchase agreements. Copper operations particularly benefited from clean electricity contracts.
Fugitive emissions from coal mines contributed 25 per cent of resource sector emissions. Diesel fuel combustion accounted for 20 per cent of mining industry emissions. On-site power generation represented 11 per cent of total sector emissions.
Global Technology Partnerships Accelerate Progress
Fortescue established partnerships with four international green technology companies. BYD collaboration focuses on electric vehicle technology and battery storage systems. LONGi partnership leverages advanced solar technology for Pilbara operations.
XCMG agreement centres on developing battery-electric mining equipment including heavy vehicles. Envision Energy cooperation targets wind power generation and energy storage solutions. These partnerships combine global expertise with Australian operational knowledge.
Nabrawind acquisition strengthened Fortescue’s wind energy innovation capabilities. The Spanish renewable technology company adds European engineering expertise. International partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange between different technological strengths.
Economic Benefits Drive Adoption Decisions
Diesel fuel represents up to 40 per cent of underground mine energy costs. Substantial expense combined with logistical challenges makes electrification economically attractive. Greenbushes Lithium Operations reduced fuel consumption by 35 per cent since 2021.
Ventilation requirements decrease by up to 50 per cent with fully electric underground fleets. Underground gold mines save $3 to $5 million annually in ventilation costs after electrification. These operational savings offset initial equipment investment requirements.
Northern Star’s Jundee mine documented 28 per cent maintenance cost reductions after fleet electrification. Electric vehicles require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. Reduced complexity eliminates traditional engine maintenance requirements.
Also Read: Why Dysprosium, Neodymium & Praseodymium Are The Rare Earths Investors Should Watch Now
Regulatory Framework Supports Industry Transformation
Australia’s Safeguard Mechanism requires covered entities to reduce carbon footprints annually. Mining companies represent 132 of 219 entities under the scheme. Regulatory pressure accelerates decarbonisation technology adoption across the sector.
Six sector-specific decarbonisation plans support national emissions targets. Mining and resources represent one focus area for government policy development. Climate Change Authority provides independent advice on policy effectiveness.
Net Zero Economy Authority coordinates Australia’s economic transformation towards emissions reduction. The agency supports achievement of net-zero emissions by 2050. Government frameworks enable low-emissions technology development and deployment.
Critical Minerals Demand Increases Urgency
Global transition to renewable energy increases demand for critical minerals. Electric vehicles require six times more critical minerals than conventional cars. Lithium, copper, graphite, zinc, cobalt, and nickel demand accelerates substantially.
Meeting electricity storage demands alone requires 50 new lithium mines, 60 nickel mines, and 17 cobalt mines globally. Global mining investment must increase by $100 billion annually to produce required commodities. Australia positions itself to supply minerals for global energy transition.
Failure to mine critical minerals creates bottlenecks for net-zero implementation. Shortages increase renewable technology costs reducing widespread adoption likelihood. Sustainable mining practices become essential for global climate goals.
Future Technology Development Continues
Mining equipment manufacturers develop custom electric solutions for Australian conditions. Partnerships with Komatsu and Caterpillar ensure equipment meets specific operational requirements. Technology adaptation addresses unique challenges of remote Australian sites.
Digital tools and artificial intelligence optimise mining operations reducing energy consumption. Sensors and advanced analytics monitor and control energy use patterns. Predictive maintenance extends equipment life while reducing overall carbon footprints.
Waste heat recovery systems capture exhaust energy during processing operations. Recycled energy reduces overall site consumption and operational costs. Energy efficiency measures complement renewable energy adoption for maximum emissions reduction.
The Australian mining industry demonstrates global leadership in decarbonisation through comprehensive strategies combining renewable energy, electrification, and innovative technologies. These initiatives position Australia at the forefront of sustainable resource extraction while supporting global climate objectives through responsible mineral supply.